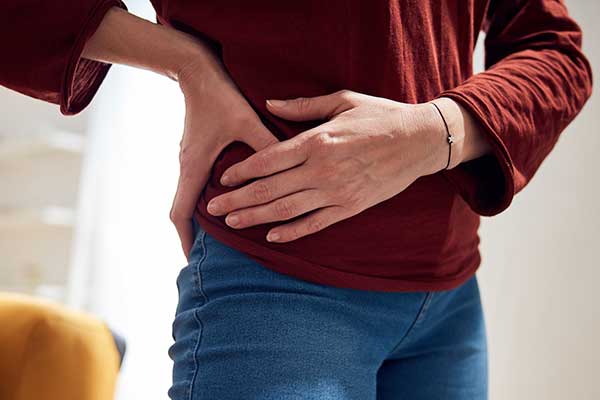
Osteitis pubis is a painful inflammatory condition that affects the joint at the front of your pelvis, as well as the ligaments and abdominal muscles that attach to it.
What causes osteitis pubis?
It is thought to be caused by repetitive microscopic tearing that occurs when your legs move apart from each other quickly or forcefully.
For this reason it is common among people who play sports such as football, rugby and hockey.
It is also associated with certain surgical procedures and with pregnancy and childbirth.
What are the symptoms of osteitis pubis?
For most people:
- You experience pain across your groin region.
- The pain is also felt in your lower stomach.
- The pain is worse when you run, kick or change direction abruptly.
- Sneezing and coughing can cause the pain.
For some people:
- You may experience discomfort when going upstairs.
- You may experience a feeling of weakness.
- You may find yourself limping or feeling that your pelvis is ‘crooked’.
How is osteitis pubis diagnosed?
If you have any concerns about pain in your groin area, you should make an appointment with your doctor, who will usually be able to make a diagnosis without the need for a scan.
While osteitis pubis is generally not serious, there are other possible causes of groin pain. Although rare, some of these are more serious, such as testicular cancer in men, which may need to be ruled out. (Regular self-examination of the testicles is recommended and can help with your doctor’s diagnosis, as well as your own peace of mind.)
Osteitis pubis can also be an indication of another issue with the muscles or the joint in your pelvis and it may be that this needs to be looked at before the osteitis pubis can be treated.
What are the treatment options for osteitis pubis?
If you have been diagnosed with osteitis pubis, it is recommended that you take a rest immediately from the type of activities that are likely to aggravate your symptoms.
During the first few days, take things easy and concentrate on managing the pain. Paracetamol-based painkillers and anti-inflammatory medication such as Ibuprofen can be helpful. You could also apply gentle heat or ice to your groin area. (Do not put ice directly next to skin as it may cause ice burn. Wrap it in a damp tea towel.)
As the pain eases and you feel comfortable resuming your day to day activities, try to add in some gentle exercises, but do not resume strenuous exercise or sport until you feel able to do so without pain. Your doctor or physiotherapist may suggest alternative exercises.
What is the prognosis (outlook) for osteitis pubis?
Provided the likely causes of the episode have been addressed as well as the symptoms, osteitis pubis should go away by itself and need not return.
If your symptoms have not cleared up, ask your GP for advice. They may recommend another kind of treatment, such as physiotherapy.
If your symptoms do not respond to physiotherapy, rest and exercise, your doctor may also recommend an injection. They are unlikely to recommend surgery unless all other options have been exhausted.
How can I prevent recurrence of osteitis pubis?
Although osteitis pubis can have many causes and not all of these are fully understood, there are certain factors that may have led to your condition. Making changes to these should help you to avoid another episode.
Try to improve your posture when sitting and standing. Look at your kicking, running and walking technique to see if it can be improved. Work on your balance, flexibility and muscle strength, particularly your core strength and gluteal muscles, which may be causing other muscles to overwork themselves.
Without noticing, you may also have altered the way you breathe in order to stabilise your pelvis. Your physiotherapist can help you relearn the correct techniques.
Pocket Physio | Download now
Search for ‘Pocket Physio’ on the Apple App Store for iOS and the Google Play Store for Android to download for free.




