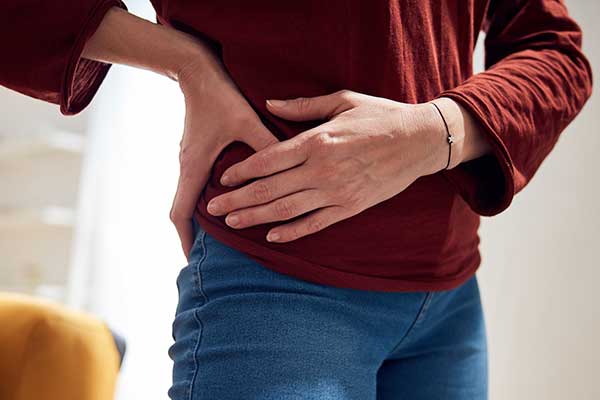
Groin strain is pain in the groin/inner thigh area.
It usually relates to overworking the adductor muscles in the inner side of your leg. For this reason, groin strain may also be referred to as adductor strain.
Overuse of these muscles can also lead to a tendon injury called adductor tendinopathy.
What causes groin strain?
Typically, groin strain is caused by overloading or overstretching of the muscles. This often occurs in sports that involve sharp changes of direction.
The pain may come on suddenly or build up through repeated activity.
You might also get a strain if your leg slips unexpectedly, such as on a wet surface.
What are the symptoms of groin strain?
For most people:
- You experience a deep, sharp pain and tenderness in your inner thigh/groin area.
- You feel the pain when walking and running and it gets worse if you change direction quickly.
- You feel the pain when getting into and out of a car, or bed.
For some people:
- The pain can be higher up in the groin or in the middle of your leg.
- You feel the pain when you press your knees together.
- There may be bruising or swelling visible.
How is groin strain diagnosed?
If you have any concerns about pain in your groin area, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
While groin strain is not serious and can be self-managed, there are other possible causes of groin pain. Although rare, some of these are more serious, such as testicular cancer in men, which may need to be ruled out. (Regular self-examination of the testicles is recommended and can help with your doctor’s diagnosis, as well as your own peace of mind.)
What are the treatment options for groin strain?
With a muscle injury like groin strain, it is important to keep moving as much as the pain allows.
Take steps to manage the pain, and do not return to sport until the pain has gone, but do try to resume normal daily activities as soon as possible.
It is beneficial to begin rehabilitation exercises as early as you can. Your doctor or physiotherapist will be able to advise you, or you could progress through your own selection of exercises to gently increase range of movement and gradually build up strength. Avoid overstretching during any exercise or activity.
Put an ice pack on your groin/inner thigh area for 10-20 minutes, three or four times a day, to relieve pain. (Do not put ice directly next to skin as it may cause ice burn. Wrap it in a damp tea towel. Remove the pack if irritation increases. Allow the area to return to normal temperature before reapplying the ice.)
It might help to compress your thigh with a tubular bandage or neoprene support, this support must be removed overnight whilst in bed. You can also use pillows or cushions to elevate your leg above the level of your heart. These methods can help to relieve pain and reduce any swelling that might be present.
You could try anti-inflammatory painkillers such as Ibuprofen. Some anti-inflammatory painkillers also come as creams or gels, which you can rub over your groin area. These tend to produce fewer side-effects than those taken by mouth. If you cannot take anti-inflammatory painkillers, other painkillers such as paracetamol, with or without codeine added, may be helpful. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
What is the prognosis (outlook) for groin strain?
Groin strain will usually resolve itself, particularly if you follow the advice here, but recovery may take 4-12 weeks depending on the severity of the strain.
If the symptoms have not gone away, ask your GP for advice. They may recommend another kind of treatment, such as physiotherapy.
How can I prevent recurrence of groin strain?
It is important not to overdo your recovery exercises or to return to sports too early.
However, it is also unwise to avoid exercise, as this can lead to further problems.
Performing regular stretching and strengthening exercises could help avoid future episodes of groin strain. So can warming up properly before exercise.
Pocket Physio | Download now
Search for ‘Pocket Physio’ on the Apple App Store for iOS and the Google Play Store for Android to download for free.




